2.Material:
RINGS & BALLS vacuum degassed, high carbon chromium bearing steel GCr15 is the standard material for precision bearing rings and balls. The material has uniform specification as AISL 52100(America)DIN100 Cr6(German),JISSUJ2(Japan)
RETAINERS-LB standard bearing retainers are made from cold rolled carbon steel
3
.precision grade: P0/P6/P5/P4
4.OEM service
5. Printing Words : we can print the any words on products under authorization legally.
6.Quality Guarantee : The items can be replaced or refunded beause of quality problem within one year from the date the buyer get the goods .
Inspection and Test
In the whole course from purchasing of raw materials to every process of production, "LB"Brand besrings are all strictly and carefully inspected to guarantee quality.Besides the basic and normally used testing instruments,the company also adopts the following testing and inspecting instruments to control the production processes and finished products.
No. Model No.of instrument
Name of instrument Test item
(1): HV-4B Pc high-speed automatic carbon and sulfur analyser Chemical composition of raw material
(2): HC-II High-speed digital display automatic analyzer
(3): 4X1 Metallurgical microscope Analysis of material and metallurgical structure
(4): Y9025 Roundness measuring equipment Roundness of groove and outer diameter
(5): R902 Groove curvature inspecting instrument Groove curvature and groove shape
(6): SRM-1 Surface roughness inspecting instrument Roughness of groove and surface
(7): S0910 Bearing vibration inspecting instrument (Accelerationg)vibration and abnormal sound
(8): BVT-1 Bearing vibration inspecting instrument (speed) vibration and abnormal sound
Installation
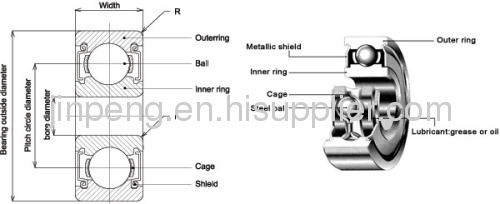
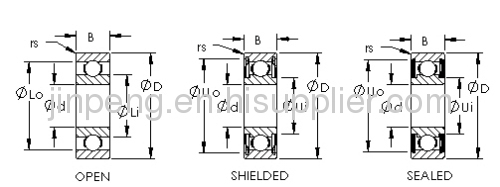
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between thebearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this by using at least two races to contain the balls and transmit the loads through the balls. In most applications, one race is stationary and the other is attached to the rotating assembly (e.g., a hub or shaft). As one of the bearing races rotates it causes the balls to rotate as well. Because the balls are rolling they have a much lower coefficient of friction than if two flat surfaces were sliding against each other.
Ball bearings tend to have lower load capacity for their size than other kinds of rolling-element bearings due to the smaller contact area between the balls and races. However, they can tolerate some misalignment of the inner and outer races.